rock fall
Detailed studies of rockfalls following the guidelines set out in the Austrian standard ONR24810 "Protection against rockfalls - terminology and definitions, effects, calculation of structures, inspection and maintenance"
Detailed studies of rocky block falls through the application of what is established in the Austrian technical guide ONR24810, currently the only existing regulation worldwide that regulates how these studies should be carried out, and how the characteristics that the protections should have should be calculated.
The Austrian standard ONR24810 was born with the need to provide a guide for the sizing of protection structures against falling rock blocks, since both the European standard EAD 340059-00-0106 and the Swiss standard FOEN and the Austrian standard WLV only They are used to certify dynamic protection barriers and at no time do they mention how the protection structures should be sized.
In the absence of an international consensus on how to carry out the dimensioning of the protections, the Austrian authorities drafted, in 2013, a standard that would establish the steps for a correct dimensioning of the protection structures. Thus was born the ONR24810 Protection against rockfalls - terminology and definitions, effects, structural calculation, inspection and maintenance, which is not only applied in Austria but also in other countries.
The ONR24810 standard is based on the "Consequence Class" of a protective structure, according to the criteria in the following table:
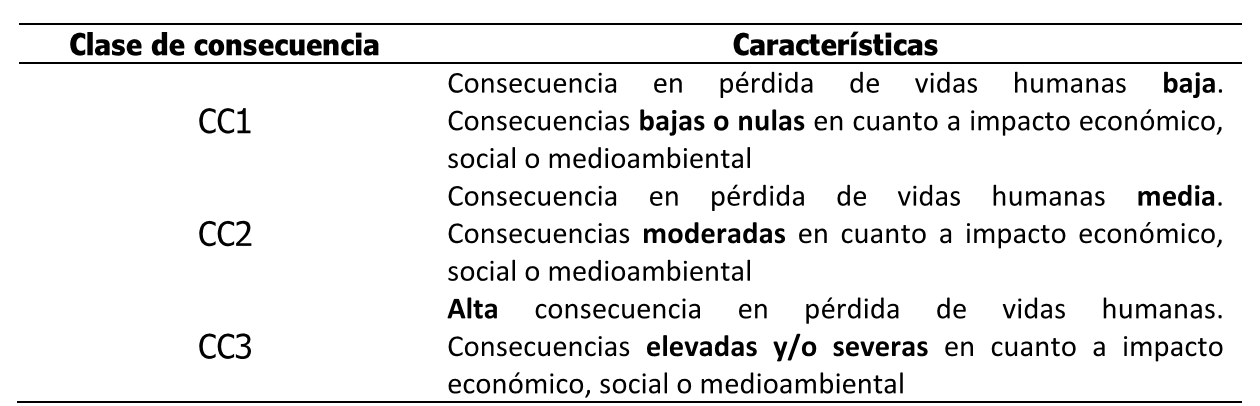
La Consequence Class (according to EN 1990:2013 Eurocode – Basis of structural design) can be defined as the qualitative assessment, in the event of system or component failure, classified with respect to the degree of loss of human life and economic impacts , social or environmental associated.
Once it has been determined what type of infrastructure to be protected (depending on the Consequence Class), it is necessary to determine the Frequency Class to determine a standard block volume whose simulation will give energies and rebounds that, having applied a safety factor, determined in ONR24810, it will establish the criteria for the sizing of the protections.

Finally, when designing the protections, an additional safety factor is applied, both to the energy and to the rebounds of the blocks, for a correct and efficient dimensioning of the protections. Likewise, some reduction factors are applied both in the energy and in the nominal heights of the existing protections in the market, given that an impact in a sensitive area could cause a decrease in the effectiveness of the protection.